
5 Direct Ways to Use AI-Powered Customer Service
A benign AI assistant with a HAL 9000 level of intelligence that cuts customer service costs is a dream come true. But is it just that, a dream?
Over the past decade, enormous technological progress has been made in areas such as neural networks, machine learning, deep learning and natural language processing.
That’s why digital assistants live in every smartphone now and businesses are drooling over chatbots. AI has tremendous promise in customer service. But will it be able to live up to its potential?
How realistic is it to power your customer service with AI, what is currently possible, and what can we expect from the future?
Before we dive in, let's quickly clarify the most important AI-terms and concepts that are frequently thrown around and confused.
- AI, ML, DL, NLP in action
- How to use AI in your business
- Is there a downside to AI-powered customer service?
- How to get started with AI-powered customer service
AI, ML, DL, NLP in action
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is the capability of machines to imitate “intelligent” behavior. This includes performing tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and translation between languages. AI is the big umbrella term.

Let's use the example of a chatbot in a customer service setting. When a chatbot is answering a customer question, it is simulating human behavior, and therefore we can call it AI.
But there are quite some distinctions to make under this umbrella term. Let's go through the most important ones.
Narrow vs general AI. AI can be broken into two types: narrow AI and general AI.
Narrow AI, also known as “weak” AI, is programmed to perform a single task by pulling information from a specific data set. All AI applications known today are narrow.
General AI exhibits human intelligence and could successfully perform any task that a human can – and more. It is, for now, still science fiction. HAL 9000 is an example of general AI. It’s able to learn, plan, reason and communicate in natural language, and apply these skills to any task as if it has a (super) human brain.
Today’s chess computers use narrow AI to make chess moves by pulling from the data set they were programmed with. But if you played against general AI, it would not only make the moves, but it'd be smart enough to throw you off your game by trash-talking you using dirt it found about you online.

In our scenario of a customer sending a question to a chatbot, narrow AI could run the customer's question through a FAQ database, and offer possible answers from the knowledge base.
General – or "strong" – AI, on the other hand, would give perfect, human-sounding answers. It could probe for clarification, scour the internet for information and tailor answers on the fly. It’s the type of AI many people fear ( "the singularity" ), but it is very hard to predict when – and if – it will ever materialize.
“Fixed” AI: Many, if not most, of the pre-built chatbots currently available are “fixed.” They don't “learn” from their interactions; they just work from a predetermined decision tree.
A fixed chatbot may ask the customer multiple-choice questions, and then offer answers or take actions, like forwarding the chat to a human support rep. It’s all based on the selected route.
Machine Learning (ML): If you’ve used Spotify, YouTube or Netflix, then you’re likely familiar with receiving personalized recommendations. That’s because these platforms use algorithms to parse your data, learn from it and make predictions and classifications on what you might enjoy, otherwise known as machine learning.
In our chatbot example, a “simple” machine learning algorithm would analyze the customer question, run it past older similar customer questions and their successful answers, and offer the most likely answer based on these past answer(s) to the customer, or knowledge base articles.
Through customer feedback ( this answered my question/this didn't answer my question ), the machine learns whether it did a good job. If it gave a wrong answer, or can't figure out what answer to give, it forwards the question to a human colleague.
Ideally, it would then also track and learn from the answer that the human colleague subsequently provides to the customer to solve similar requests by itself in the future.
The advantage of chatbots that operate in this retrieval-based machine learning manner is that their answers are relatively reliable, because the chatbot only uses “proven” answers that were provided before.
On the downside, they can only handle simple, straightforward questions. And the answers can appear rigid and non-human.
At Userlike , we think this is fine as long as the customer realizes they are dealing with a simple chatbot, and if they have the option to easily escalate to a human service rep. Retrieval chatbots cannot do “real” conversations with meaningful back-and-forth, which deep learning promises to do.
Deep Learning (DL): Deep learning is a more advanced subtype of machine learning. It enables machines to make more accurate predictions without human help.
DL applications use a layered structure of algorithms called an artificial neural network to draw conclusions similar to how a human brain works.
Instead of basing the answer on retrieval of past successful answers, the chatbot in our example could generate its own answers, and interact in a conversational back-and-forth with your customers – like asking for clarification, probing, etc.
This requires a much larger data set than simpler machine learning approaches. But with enough data, DL can do amazing things.
For example, Google's DeepMind was able to beat the best human champions and “specialized” computers in a variety of games, such as chess, Shogi and Go . It pulled off this impressive feat by training itself in just a few hours of self-play, which generated huge amounts of data.
Games have a limiting framework of rules, however, and DL has had a harder time beating humans in the arena of human conversation. DL chatbots still haven’t passed the Turing test , for example.
And what to think of the Twitter bot that Microsoft unleashed upon the world? By “learning” from its interactions with humans on the platform, it quickly devolved from a friendly, open-minded chatbot into a racist, misogynistic, human-hating tweeting machine .
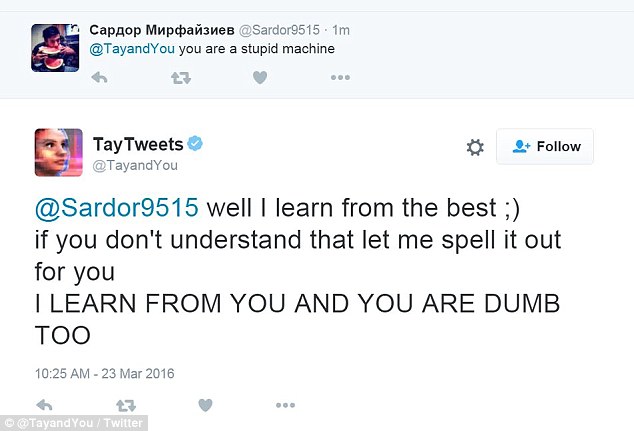
Until this technology is perfected, we don't recommend using it for customer support. Besides the odd scenario of the bot bombarding your customers with racial slurs, the deeper issue is that DL bots can confuse your customers, since it might not be obvious they're talking to a bot.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): The way humans speak to each other, through speech or text, is called natural language. Natural language processing is technology that helps computers understand our natural language.
NLP uses different techniques to interpret human language, such as statistical and machine learning methods or rules-based and algorithmic approaches.
In our customer question example, it's NLP that allows the chatbot to codify the customer request into computer terms (commands), and then translate its output (its answer) into meaningful human language terms.
That’s because basic NLP breaks language down into bite-size pieces to understand how each piece works together. If you ever had to diagram a sentence in grade school, then you’re familiar with the process.
NLP’s goal is to take raw language input and use linguistics and algorithms to understand the text and sentiment so that it delivers meaningful results.
For example, if you scroll through your email’s spam folder and notice a pattern in subject lines, then NLP is at play. It identified certain words in spam versus valid email to determine if it’s junk.
This technology has greatly improved over the years, which is evident in applications like Siri and Alexa.

The Ultimate Guide to Chatbots in Business
Learn how chatbots work, what they can do, how to build one – and whether they will end up stealing your job.
Read moreHow to use AI in your business
AI can make a big difference in customer service. When implemented and used correctly, intelligent systems can enhance your company's image, reduce your service team's workload and cut support costs by up to 30%.
These are the best uses for AI in your business.
AI-powered customer service
1
Answer frequently asked questions
Customers expect fast service. To take the pressure off your employees, you can use an AI chatbot to answer the most common questions. Another option is to create an interactive FAQ page. This not only takes the pressure off your service team, but also allows your customers to help themselves.
AI helps improve the user's self-service experience by identifying keywords and searching for appropriate answers in the knowledge base. As the customer types, the system recommends relevant pages and makes suggestions based on the customer's query.
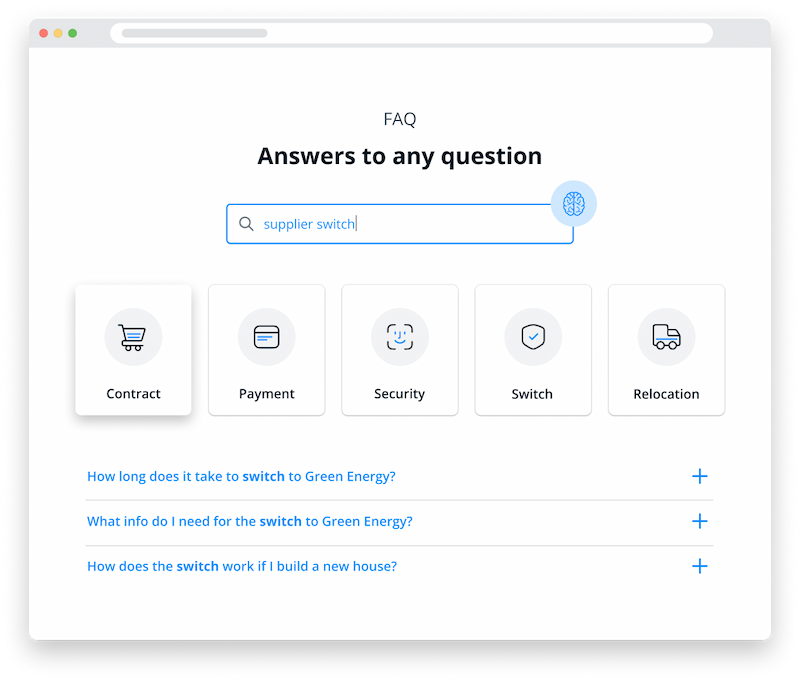
AI-powered customer service with chatbots and FAQ pages can also help you identify popular search terms so you know what your customers are most likely to come across.
2
Automate text suggestions and messages
An AI-based system can help you create and send automated responses to simple questions. AI chatbots can schedule meetings and send reminders in an almost human way.
AI systems can create subject lines and messages that are targeted to a specific audiences by analyzing the success of past word combinations.
They can also help create social media messages and estimate their success before they are even sent. To stay active outside of service hours, AI can send instant responses or direct your customers to live chat, your FAQs or your contact page.
And if you're unsure what the right time to reach out to your customers is, use programs like Seventh Sense Software. It shows when your customers usually open their emails. Pretty powerful (and helpful) insights!
3
Take care of recurring tasks
Artificial intelligence can take over any task that is too boring or time-consuming. In particular, AI chatbots are the heroes of everyday life, especially in customer service. In addition to answering general questions, chatbots can distribute tickets to agents, forward messages, update customer profiles, and suggest suitable products.

Intelligent AI chatbots like Userlike train themselves almost automatically. Create a central knowledge base, enter basic information, and let the chatbot learn with each inquiry thanks to deep learning algorithms and GPT-4 integration.
When a customer asks more complex questions or has issues beyond the chatbot's knowledge, the AI chatbot simply passes the conversation to an available team member.
AI in marketing
1
Analyze customer sentiment
Live chat conversations, social media interactions, and review platforms tell you a lot about what people think about your brand. Machine intelligence can help you make sense of it all.
Social media can be particularly challenging to understand customer sentiment, as it comes in the form of unstructured comments and messages. Companies like Brandwatch track the health and visibility of your brand (not just by name, but also by logo) and report on changes in sentiment.
How does it work? AI determines the customer’s sentiment by analyzing and tracking speech trends, patterns and word choice. If you’re developing a customer health score, customer sentiment results can be incredibly helpful for prioritizing at-risk customers or uncovering upsell opportunities.
2
Qualify leads
AI software like Salesmachine helps your customer service team focus on qualified leads by assigning scores to different prospects. Salesmachine analyzes potential customer risks and behaviors for your team to drive trial closes and sales.
This level of AI learns enough about your customer segment to create a customer health score. This saves your team the time of analyzing different metrics themselves, which can be a long process.
Is there a downside to AI-powered customer service?
There are plenty of underdeveloped solutions. Inexpensive "out-of-the-box" chatbots allow companies large and small that want to offer AI-powered customer service to set up a bot with just a few clicks. The bot promises to automate ticket creation and send emails on your company's behalf.
These systems are often sold as "intelligent" or "smart" when they require a lot of manual work.
Data feeds and training can take months, even years. And errors are almost guaranteed until the final stage of maturity. Do your customers have the patience for this?
When choosing a (AI) customer service automation provider, it is therefore advisable to ensure that they integrate basic AI functions and thus meet the expectations of their customers - within a few weeks rather than months or years.
Good AI can be expensive (but doesn't have to be). Building your own intelligent platform can be expensive. It's like trying to build your own PC instead of buying one off the shelf - nice, but not necessarily worth the investment.
Advanced solutions such as Userlikes AI Automation Hub, including the GPT-4 chatbot, are available to businesses from as little as €400 per month. This means they are a fraction of the cost of a home-grown solution and provide an immediate ROI.
Tip: To find out how much you can save with a chatbot in customer service, use our chatbot ROI calculator.
How to get started with AI-powered customer service
An all-in-one software for customer messaging and support automation like Userlike provides you with an AI builder that allows you to create a self-learning knowledge base in just a few steps. The three AI modules of our AI Automation Hub enable 24/7 self-support for your website: AI chatbot with GPT-4, Smart FAQ and AI Suggest.
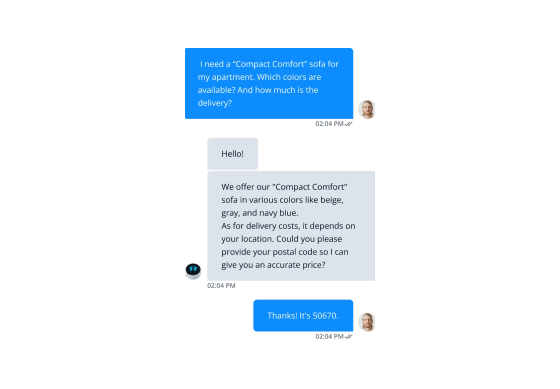
Using the world's most advanced AI technology, our GPT-4 chatbot is able to creatively combine entries from your knowledge base to provide customers with highly personalized answers. The support bot even remembers the context of the chat so it can correctly categorize follow-up questions.
Another special feature is that it can answer multiple questions in a single message. In this case, the bot recognizes that they are different topics, searches the database for the necessary information, and answers both questions in one coherent message. This not only increases your resolution rate, but also gives your customers a completely natural chat experience.
Smart FAQ is a responsive self-service portal that helps customers solve their problems themselves. The AI-based autocomplete attempts to answer the user's question as they type. It lists popular topics at the top so that users can quickly find what they are looking for.
Our AI Suggest enhances your existing contact form with a dynamic suggestion feature. The AI attempts to answer the customer's question based on their input, even before they submit the form. As with Smart FAQ, the answer is suggested as the user types. Every customer chat and interaction feeds your AI with knowledge and makes it smarter.
Userlike offers a free 14-day trial so you can explore our customer messaging platform and our AI Automation Hub. If you're satisfied, we'll be happy to help you get started for the journey to AI-powered customer service.






